end tidal co2 range high
In this phase PECO2 is close to alveolar carbon dioxide tension P A CO2. Phase III Plateau phase.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
When this occurs the alveoli come in contact with the venous side of circulation from the over expansion of the lung.

. Confirming tracheal tube placement. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. The median ETCO2 value was 32 mmHg IQR 27 38 mmHg range 18-80 mmHg.
What is end-tidal CO2. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. Assessing the effectiveness of chest compressions.
End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a measure of metabolism perfusion and ventilation. Hence that persons capnography will show a very low end-tidal CO2 level but the alveolar and arterial CO2 pressures will be much higher and increasing in time. Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for.
Where the respiratory rate is very low and the tidal volumes are very large the end-tidal CO 2 can be higher than the mean arterial CO 2. Forty-six of 96 48 95 confidence interval CI 38 58 patients had abnormal ETCO2 values including 37 39 95 CI 29 49 with low ETCO2 levels and. End tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 monitoring is the fastest indicator of ventilatory compromise.
Patients with lung. For most patients the gap between etCO2 and PaCO2 will be 5-10 mm which will leave them at the higher end of this range eg a pH of 74. In a state of perfect equilibrium arterial and end-tidal CO 2 levels correlate on a 11 basis.
High VT and low resp rates. According to the book by Hockenberry and Wilson 2015 p 1140 normal values of ETCO2 are 30-43 mmHg which is slightly lower than arterial PaCO2 35-45mmHg. Goal is 35-45 mmHg.
There was no significant change in the Q angle and the T time after treatment. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. But even in an ideal physiologic state a difference of 2 to 5 mm Hg usually exists.
In the ED we typically think of a EtCO2 as a marker of perfusion and ventilation. If a person holds his breath that persons body accumulates CO2 and its etCO 2 is going to be zero. In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg.
A very rapid increase in PECO2 which represents exhalation of mixed air. Deeper slower alveoli are able to share their gas with the capnometer whereas previously that gas would have remained in the airway. The median EtCO2 at T0 and T60 was 35 IQR.
Other important clinical conditions that may result in the etCO 2 exceeding the PaCO 2 include patient exercise and large tidal volumes. High CO2 levels result in cerebr al vasodilation while low CO2 levels result in cerebral vasoconstriction. Nasopharyngeal temperature was 389C.
Over the next 30 min the end-tidal carbon dioxide increased from 35 to 45 mmHg accompanied by a slight increase in heart rate from 95 to 105 beatsmin. The height of the ETCO2 waveform during CPR has been used as an indirect measure of adequate chest compressions helping those involved in resuscitation monitor the effectiveness of their compressions in real time. Arterial CO2 tension affects blood flow to the brain.
Reflects the alveolar expiratory flow a small increase in PECO2 which happens the peak at the end of tidal expiration ETCO2. This article was written based on dataset of Karim Basiri Sofianis specialty thesis entitled Comparison of end tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 and arterial blood bicarbonate levels in patients with metabolic acidosis referred to ED registered in Tabriz University of Medical Sciences. There was no significant change in EtCO2 after treatment.
30-38 and 34 IQR. Predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC. The shape will start high and then trail off as air leaks from the lung producing a similar high on the left lower on the right shape.
However EtCO2 is an extremely powerful surrogate for endotracheal tube ETT P osition CPR Q uality R eturn of spontaneous circulation ROSC S trategies for treatment. What does end tidal CO2 tell you. The median initial PEFR was 200 interquartile range IQR.
Known as the arterial-to-etco2 gradient this differential results from small amounts of dead-space ventilation ventilation without perfusion and a slight venous admixture. This effect could also be understood from the viewpoint of CO2 accumulation. The mean age was 37 years and 26 47 were women.
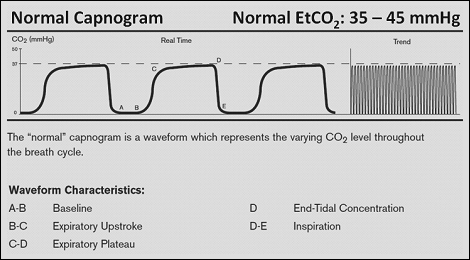
The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle. The increasing end-tidal carbon dioxide heart rate and temperature suggested a physiologic perturbation that required immediate attention and investigation. This is result of a slower expiration.
Sustained hypoventilation defined as PaCO2 levels 66 kPa results in increased cerebral blood flow and increased ICP which can harm head-injured patients. Monitoring end-tidal CO 2 ET-CO 2 provides instantaneous information about ventilation how effectively CO 2 gas is being exhaledeliminated by the respiratory system perfusion how effectively CO 2 is being transported through the vascular system to the lungs and metabolism how effectively CO 2 is being produced by cellular metabolism. Consequently a strategy of high-frequency low-tidal volume breaths will tend to achieve less CO2 clearance for.

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Pre Hospital Capnography Ppt Download

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Capnogram R Series Defibrillator Zoll Medical Uk
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Acep Now

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Potential Applications Of Capnography In The Prehospital Setting Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table
